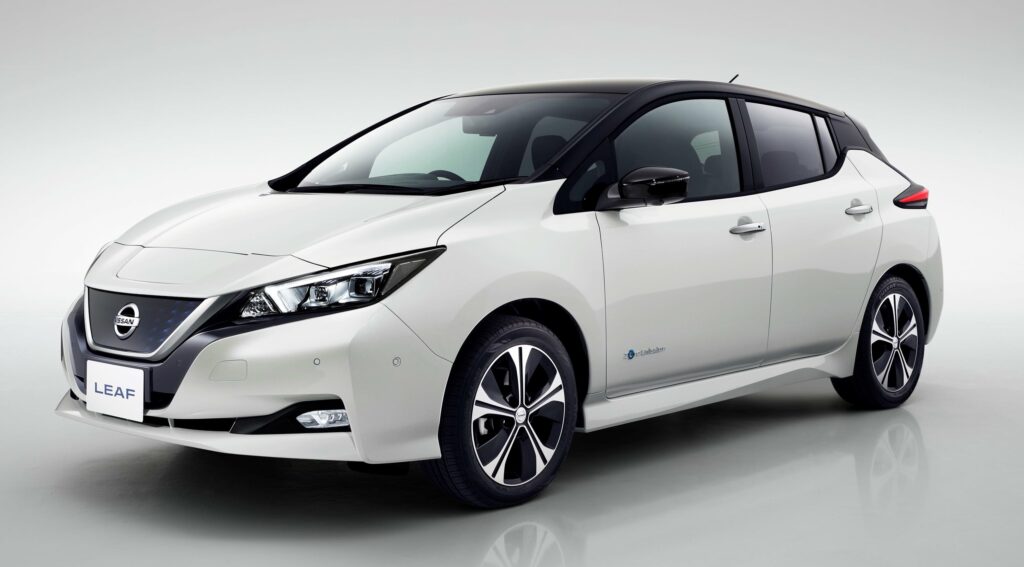
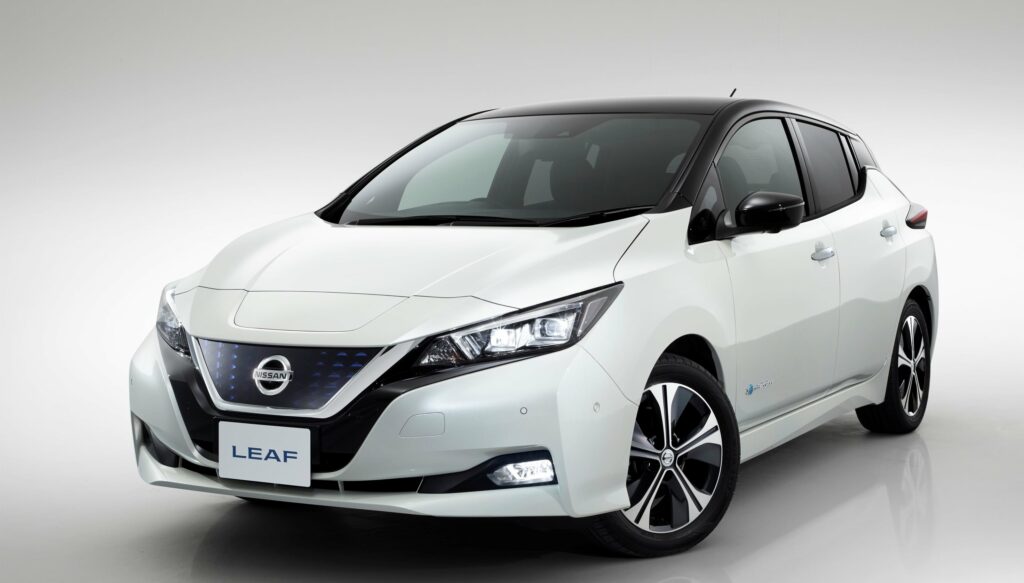
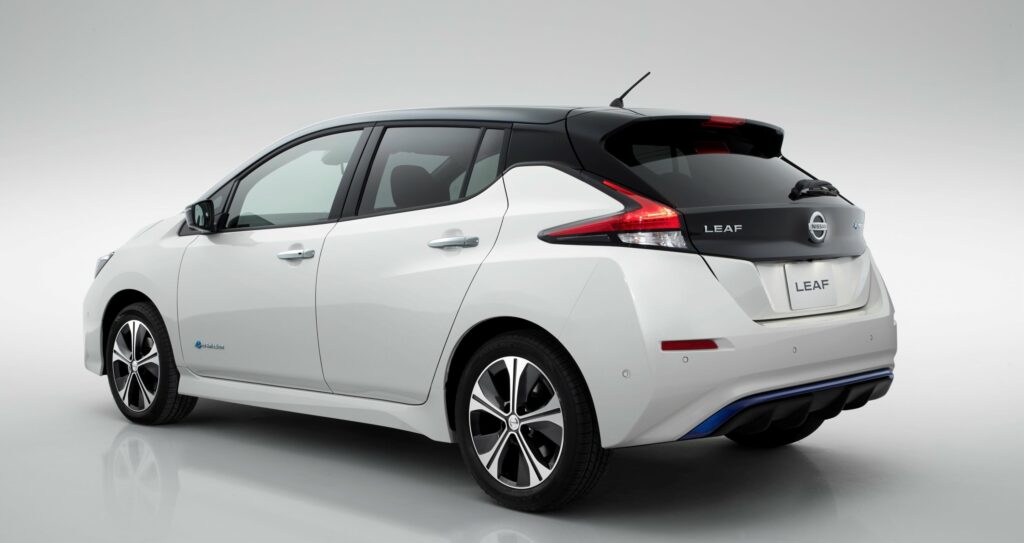
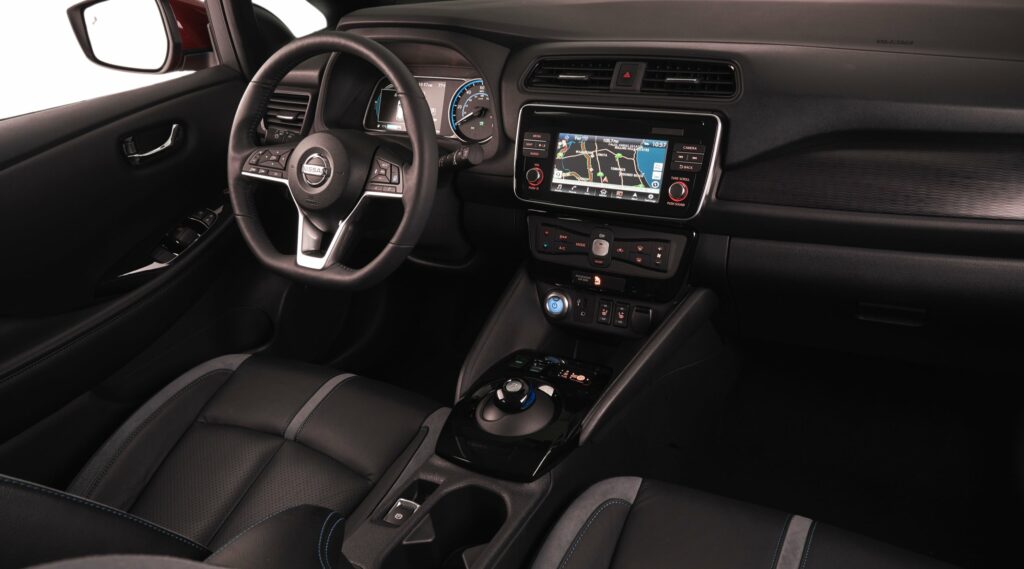
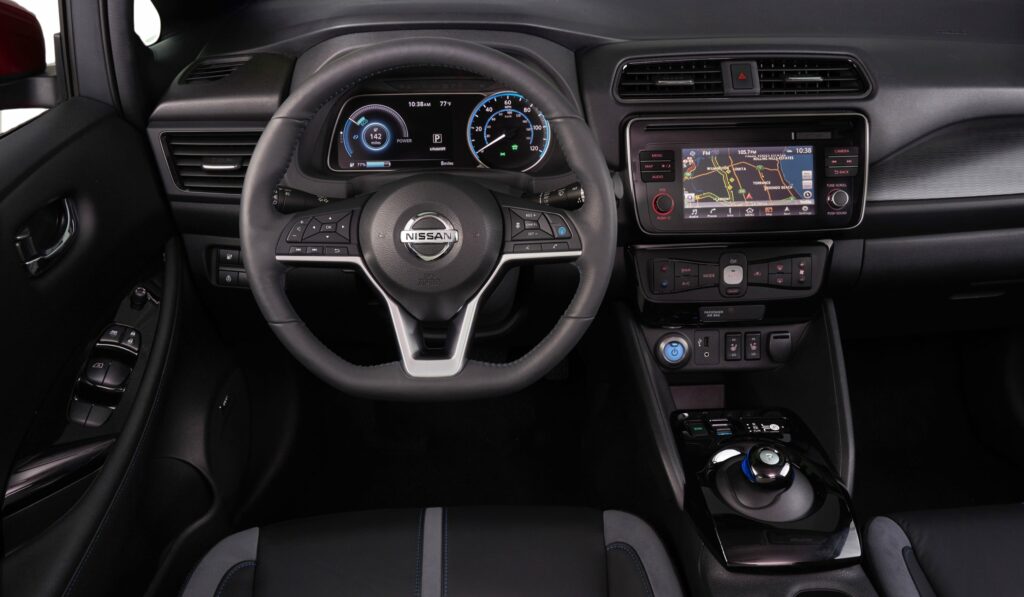
Nissan Leaf
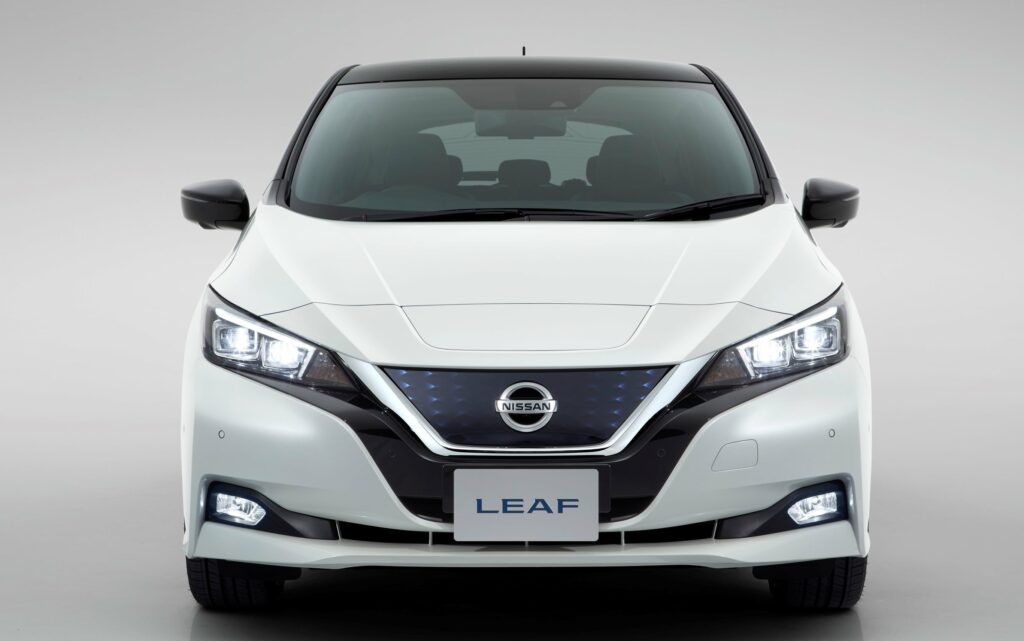
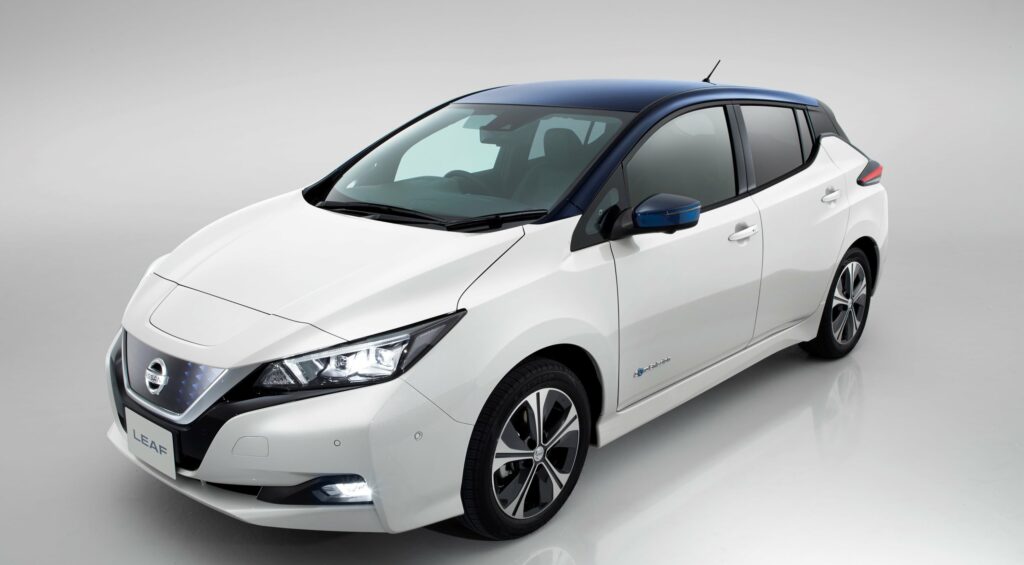
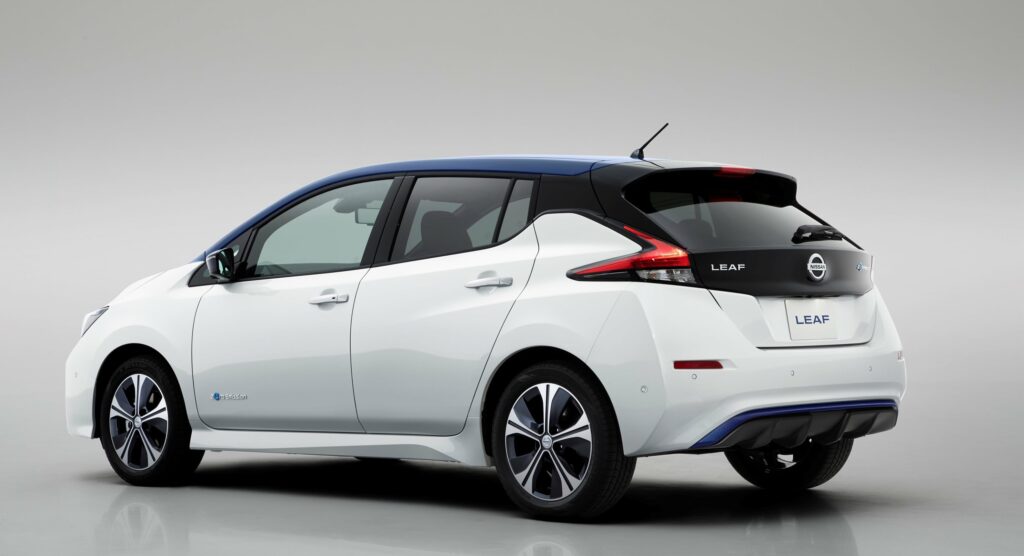
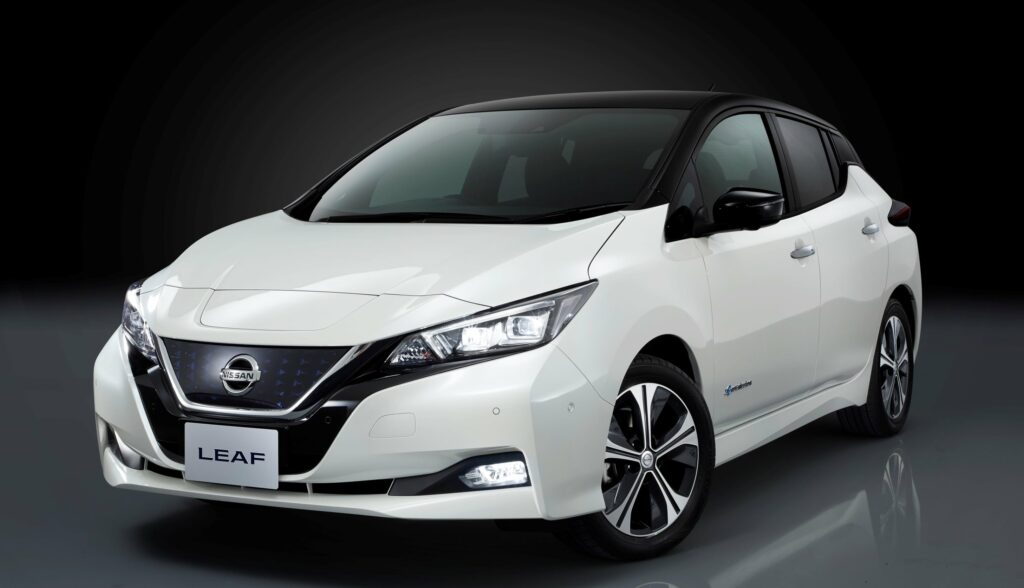
The 2018 Nissan Leaf 40kwh is a modern, eco-friendly hatchback with an updated design and power, as well as an increased range on a single charge. This car is safe for the environment because it does not emit any harmful substances into the atmosphere. The hatchback can really be called innovative, as its technical characteristics are at a fairly high level. The car is equipped with an autonomous driving system, front-wheel drive, an intelligent parking system, a smart pedal, and other useful systems. It is also characterized by a low aerodynamic coefficient, equal to 0.28.

In order to increase the maneuverability of the car on the road, the engineers involved in its creation decided to change the chassis. The location of the heavy units in the central part of the hatchback made it possible to reduce the inertial load that can occur during intermittent driving in the city. As a consequence, downforce was greater during fast freeway driving. It also helped to get extra stability when cornering. The manufacturer also decided to change the material of the rear suspension shock absorber, which reduced the stiffness when driving on rough terrain.
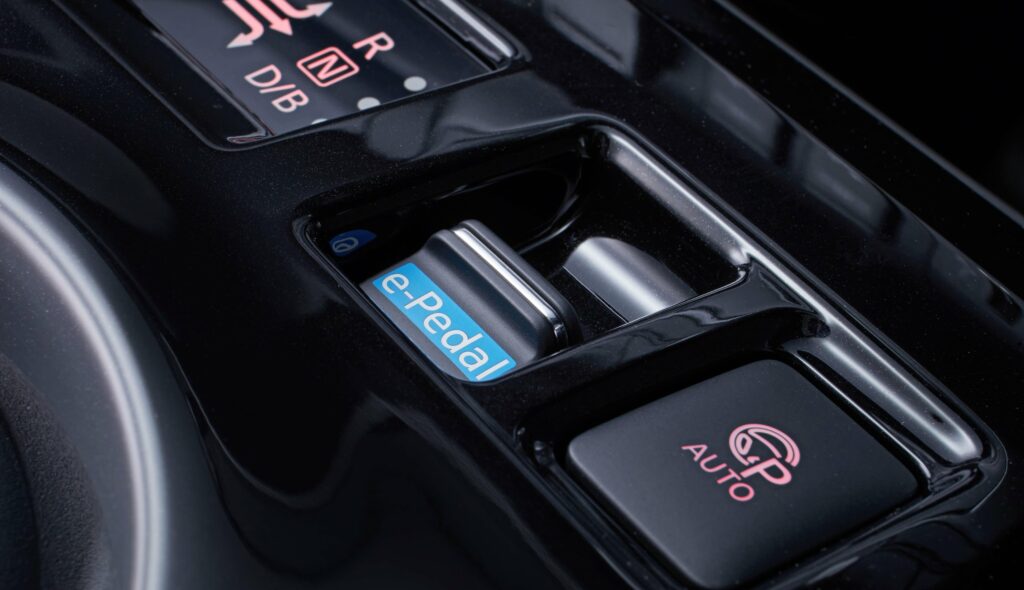
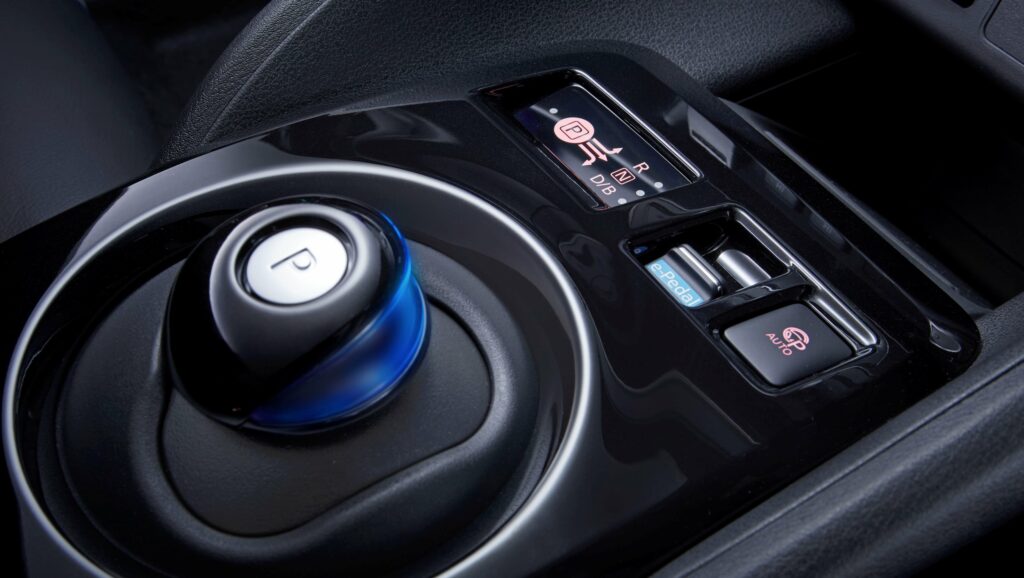
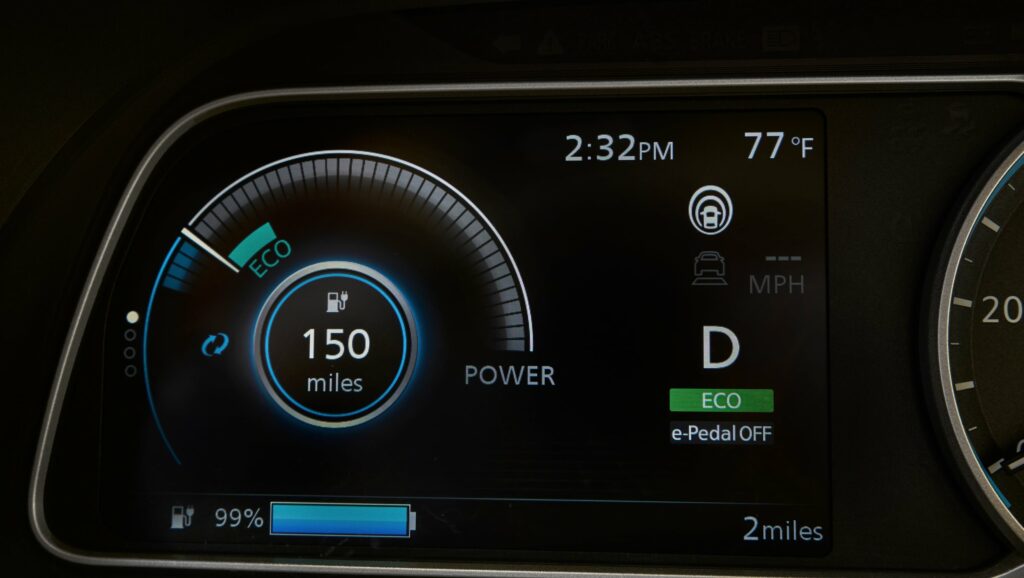
If desired, the owner of the electric car can choose the most optimal driving mode for themselves. There are three of them. The first is D (drive). It is best used for normal driving. The second mode is b (brake). It should be switched on when driving with a high degree of regeneration. ECO (third) is used for fairly quiet driving, here the power is also reduced.

The car with an electric powertrain boasts increased power (150 hp) and torque (320 Nm), as well as a more efficient distribution of energy. The design of the battery has been changed, so it was possible to increase the mileage figures. This car has a range of 378 kilometers on the NEDC cycle and 240 kilometers on the EPA cycle. The dimensions of the battery pack have not changed; they remain exactly the same as in the previous generation models. Thanks to the updates, acceleration, and dynamics have improved. The car with a top speed of 144 km/h can accelerate to the first hundred kilometers per hour in 7.9 seconds. This figure is much better than the previous generation of the model. The acceleration time was more than 11 seconds. If we talk about the volume of the battery, it is 40 kW.
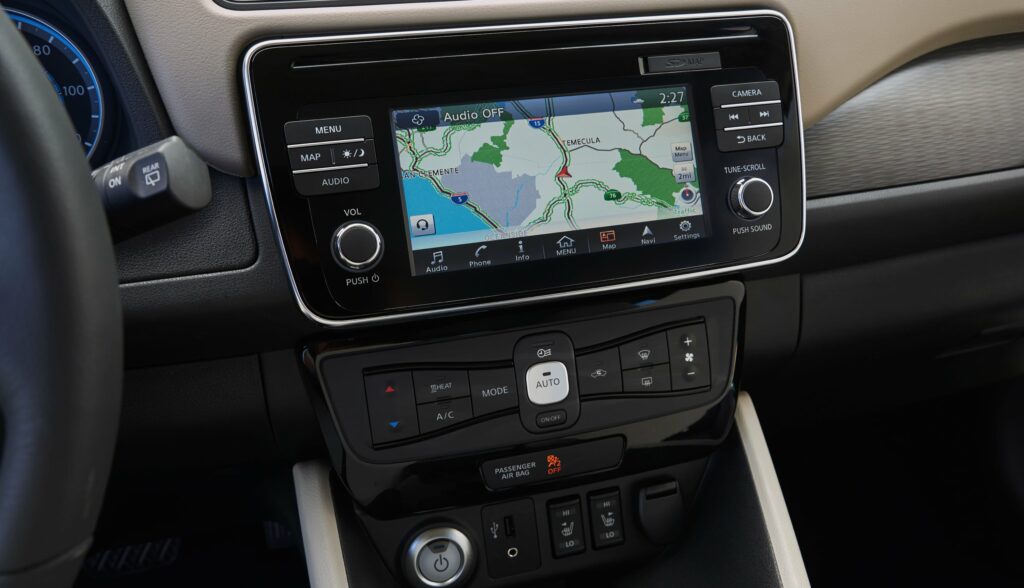
As for replenishing the battery level, here the driver can choose for himself the most optimal way. If you use a domestic network with a voltage of 220 V, the owner of the car will need about 16 hours, the accelerated charging will take 8 hours. To save time, you can charge the electric car up to 80% at the fast charging station: here the driver will spend up to 50 minutes.

One of the main innovations in this model was the integration of the electric car with the public power grid. Two-way charging is provided. This means that the electric car not only receives but also gives energy. There is even a special system responsible for smart energy distribution, i.e. excess energy is accumulated during the day and the car is recharged at night – while cheap tariffs are in effect. The difference is then made up at other charging stations.
The driver also has the opportunity to use the batteries as a mobile power source, which is able to share energy with the grid in case of various failures or a shortage of electricity. With the help of special technology, it is possible not only to make two-way charging but also in the future to earn from the sale of energy, which is a definite plus for the owner of an electric car.

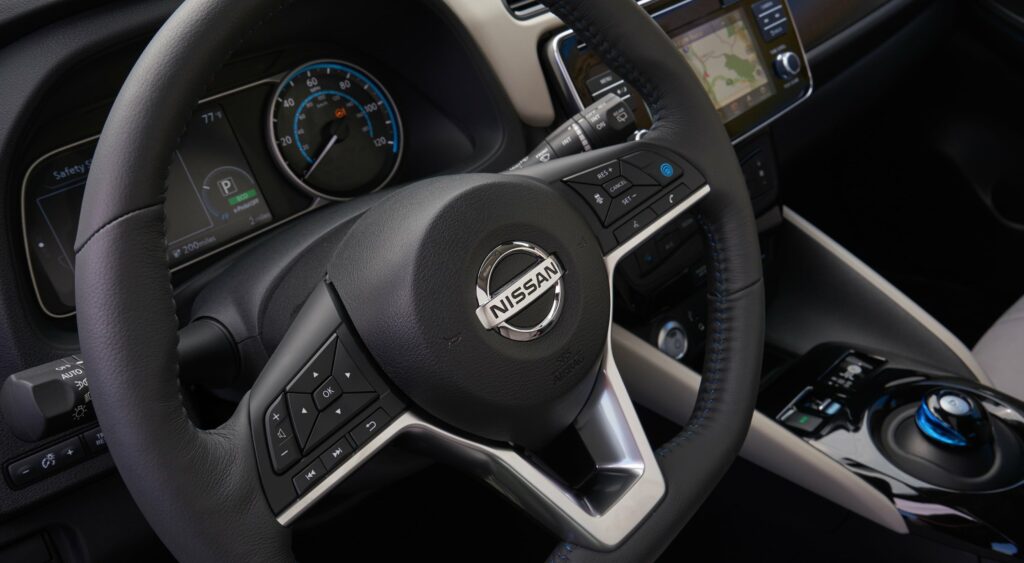
The five-door car is equipped with useful features, so-called digital assistants, which help the driver while driving. The first of them is called ProPILOT. It is responsible for the autonomous driving of the electric car. With the help of this system, the hatchback can move independently without the participation of the driver, for example, on a country highway. The movement is carried out within one lane. The electric car is able to independently gain and decrease speed, brake, and correct the trajectory. The car system independently regulates the distance to the vehicle in front. In this case, the mode initially selected by the driver is used. If the vehicle in front of you slows down, the system reduces speed or even stops the vehicle. If the person sitting behind the wheel does not press the brake pedal, the electric car will stand in one place after coming to a complete stop. The driver will be able to activate the system by stepping on the gas. The hatchback will then continue on its way.
The next useful feature is ProPILOT Park. It provides autonomous parking without driver input. Here, the electronics not only adjust the gas pedal and brake pedal but can also turn the steering wheel. The system is able to accurately determine the parking space
| Performance | |
| Acceleration 0 – 100 km/h | 7.9 sec |
| Top Speed | 144 km/h |
| Electric Range | 225 km |
| Total Power | 110 kW (150 PS) |
| Total Torque | 320 Nm |
| Drive | Front |
| Battery and Charging | |
| Battery Capacity | 40.0 kWh |
| Battery Useable | 37.0 kWh |
| Europe | |
| Charge Port | Type 2 |
| Port Location | Front – Middle |
| Charge Power | 3.6 kW AC |
| Charge Time (0->225 km) | 12h15m |
| Charge Speed | 19 km/h |
| Fastcharge Port | CHAdeMO |
| FC Port Location | Front – Middle |
| Fastcharge Power (max) | 46 kW DC |
| Fastcharge Time (23->180 km) | 41 min |
| Fastcharge Speed | 230 km/h |
| Energy Consumption | |
| EVDB Real Range | |
| Range | 225 km |
| Vehicle Consumption | 164 Wh/km |
| CO2 Emissions | 0 g/km |
| Vehicle Fuel Equivalent | 1.8 l/100km |
| NEDC Ratings | |
| Range | 350 km |
| Rated Consumption | 152 Wh/km |
| Vehicle Consumption | 106 Wh/km |
| CO2 Emissions | 0 g/km |
| Rated Fuel Equivalent | 1.7 l/100km |
| Vehicle Fuel Equivalent | 1.2 l/100km |
| WLTP Ratings | |
| Range | 270 km |
| Rated Consumption | 206 Wh/km |
| Vehicle Consumption | 137 Wh/km |
| CO2 Emissions | 0 g/km |
| Rated Fuel Equivalent | 2.3 l/100km |
| Vehicle Fuel Equivalent | 1.5 l/100km |
|
Rated = official figures as published by manufacturer. Rated consumption and fuel equivalency figures include charging losses.
|
|
|
Vehicle = calculated battery energy consumption used by the vehicle for propulsion and on-board systems.
|
|
| Real Energy Consumption between 110 – 231 Wh/km | |
| City – Cold Weather | 168 Wh/km |
| Highway – Cold Weather | 231 Wh/km |
| Combined – Cold Weather | 195 Wh/km |
| City – Mild Weather | 110 Wh/km |
| Highway – Mild Weather | 180 Wh/km |
| Combined – Mild Weather | 142 Wh/km |
| Energy use for each trip will vary considerably depending on the driver and the conditions. Therefore, we have provided a range of estimates which can be useful in developing an understanding of the potential benefits of this technology. | |
| Safety Rating | |
| Adult Occupant | 93% |
| Child Occupant | 86% |
| Rating Year | 2018 |
| Vulnerable Road Users | 71% |
| Safety Assist | 71% |
| Dimensions and Weight | |
| Length | 4490 mm |
| Width | 1788 mm |
| Width with mirrors | No Data |
| Height | 1530 mm |
| Wheelbase | 2700 mm |
| Weight Unladen (EU) | 1580 kg |
| Gross Vehicle Weight (GVWR) | 1995 kg |
| Max. Payload | 490 kg |
| Cargo Volume | 435 L |
| Cargo Volume Max | 1176 L |
| Cargo Volume Frunk | No Data |
| Roof Load | 35 kg |
| Tow Hitch Possible | No Data |
| Towing Weight Unbraked | 0 kg |
| Towing Weight Braked | 0 kg |
| Vertical Load Max | No Data |
| Miscellaneous | |
| Seats | 5 people |
| Isofix | Yes, 3 seats |
| Turning Circle | 10.6 m |
| Platform | No Data |
| Car Body | Hatchback |
| Segment | C – Medium |
| Roof Rails | No |
| EV Dedicated Platform | No Data |
Home and Destination Charging (0 -> 100%)
A public charging station is required to use the highest possible charging rate. The EVSE/charging station’s charging capacity affects how long it takes to fully charge the battery. The table below shows all possible options for fully charging the Nissan Leaf.
In Europe, plugging an electric car into an outlet is often as easy as plugging it into a household outlet, but there are differences from country to country. The table below shows the different ways to charge the Nissan Leaf, but in some countries some chargers may not be available.
Type 2 ( IEC 62196)

| Charging Point | Max. Power | Power | Time | Rate |
| Standard 3.6 kW On-Board Charger | ||||
| Wall Plug (2.3 kW) | 230V / 1x10A | 2.3 kW | 19 hours | 12 km/h |
| 1-phase 16A (3.7 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.6 kW | 11h45m | 19 km/h |
| 1-phase 32A (7.4 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.6 kW | 12h15m | 18 km/h |
| 3-phase 16A (11 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.6 kW | 12h15m | 18 km/h |
| 3-phase 32A (22 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.6 kW | 12h15m | 18 km/h |
| Optional 6.6kW On-Board Charger | ||||
| Wall Plug (2.3 kW) | 230V / 1x10A | 2.3 kW | 19 hours | 12 km/h |
| 1-phase 16A (3.7 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.7 kW | 11h45m | 19 km/h |
| 1-phase 32A (7.4 kW) | 230V / 1x29A | 6.6 kW | 6h45m | 33 km/h |
| 3-phase 16A (11 kW) | 230V / 1x16A | 3.7 kW | 11h45m | 19 km/h |
| 3-phase 32A (22 kW) | 230V / 1x29A | 6.6 kW | 6h45m | 33 km/h |
Fast Charging (10 -> 80%)
If you want to enjoy driving an electric car, one of the most important features to consider is the number of miles per hour the car can travel while charged. This is called the “range” of the car. All electric cars have a certain range, even if they are 100% charged. This is because they do not have an internal combustion engine to lean on if you need to drive a long distance.
Max. Power: The maximum power provided by the charging point
Avg. Power: The average power provided by the charging point during a session of 10% to 80%.
Time: the time it takes to charge from 10% to 80%
Speed: the average charging rate during the session of 10% to 80%
CHAdeMO

| Charging Point | Max. Power | Avg. Power | Time | Rate |
| CHAdeMO (50 kW DC) | 46 kW | 40 kW | 41 min | 230 km/h |
| Brand | Nissan |
| Model | Leaf |
| Body Style | Hatchback |
| Car Engine | electric |
| Motor power | 110 |
| Maximum Torque, Nm | 320 |
| Battery Energy, kWh | 40.0 |
| Power reserve (NEDC/EPA/WLTP), km | - / - / 225 |
| Level Charging (230/400/DC), hours | - / - / 0.41 |
| Electrical Acceleration, 0-100 km/h (0-62.1 mph) in sec | 7.9 |
| Top Speed, km/h | 144 |