Introduction: In the era of sustainable transportation, all-electric cars stand at the forefront, reshaping the way we move. These eco-friendly vehicles have captured the imagination of environmentally-conscious consumers and tech enthusiasts alike. But how do these sleek machines, devoid of traditional internal combustion engines, harness the power to zoom down the road silently? Let’s delve into the inner workings of all-electric cars.

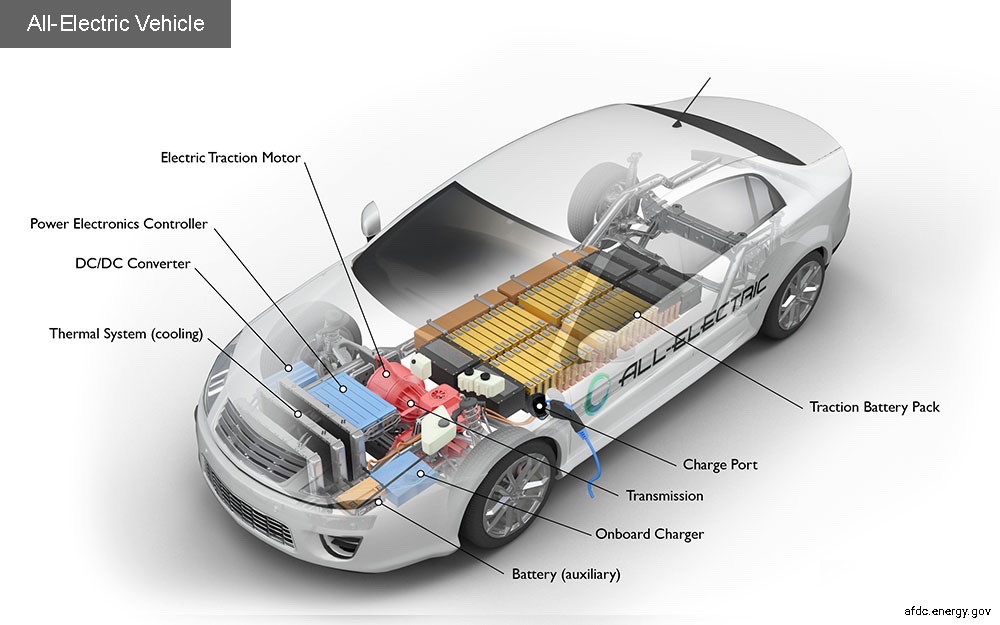
Electric Motors: The heart of an all-electric car lies in its electric motor. Unlike the familiar roar of a combustion engine, electric cars are propelled by electric motors that operate with a hushed efficiency. These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the wheels to propel the vehicle forward.
Battery Pack: Fueling this silent revolution is the battery pack, a sophisticated array of lithium-ion cells. Acting as the energy reservoir, these batteries store electricity to power the electric motor. The capacity of the battery determines the car’s range, with advancements in battery technology continually extending the distance these vehicles can travel on a single charge.
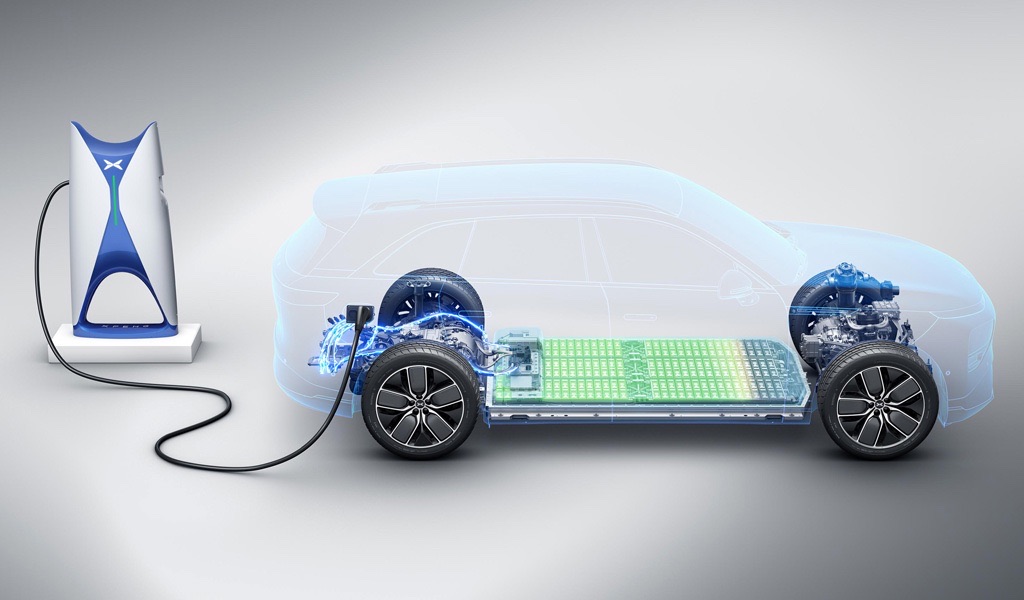
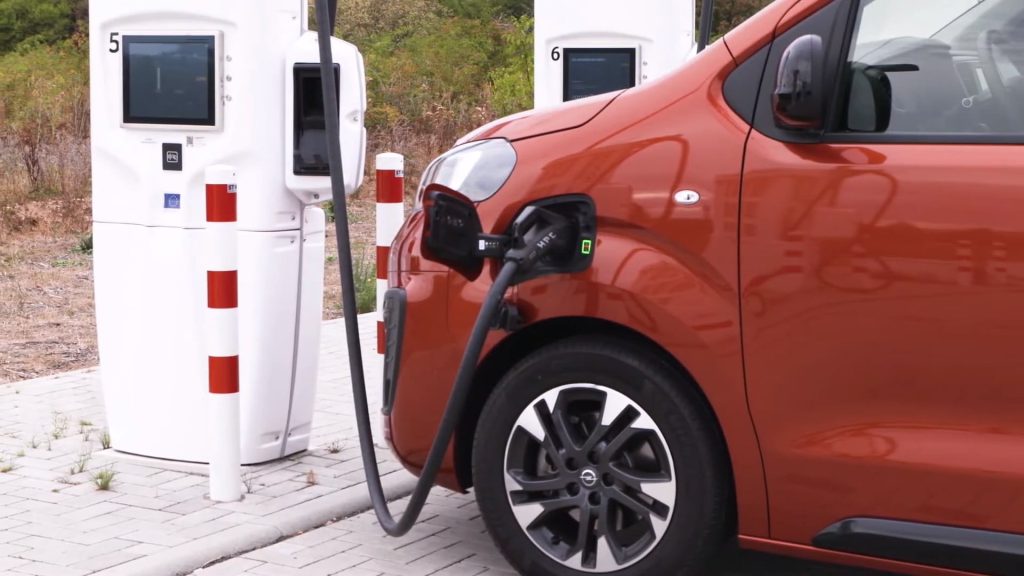
Charging Infrastructure: Charging an all-electric car is a pivotal aspect of ownership. Owners can recharge their vehicles through various methods, including home charging stations, public charging points, and the rapidly expanding network of fast-charging stations. The charging time depends on the charging level – from standard overnight charging at home to rapid charging options that can provide a significant boost in a matter of minutes.
Regenerative Braking: All-electric cars also boast an innovative feature known as regenerative braking. This technology harnesses the kinetic energy produced during braking, converting it back into electricity to recharge the battery. Not only does this enhance energy efficiency, but it also extends the overall range of the vehicle.
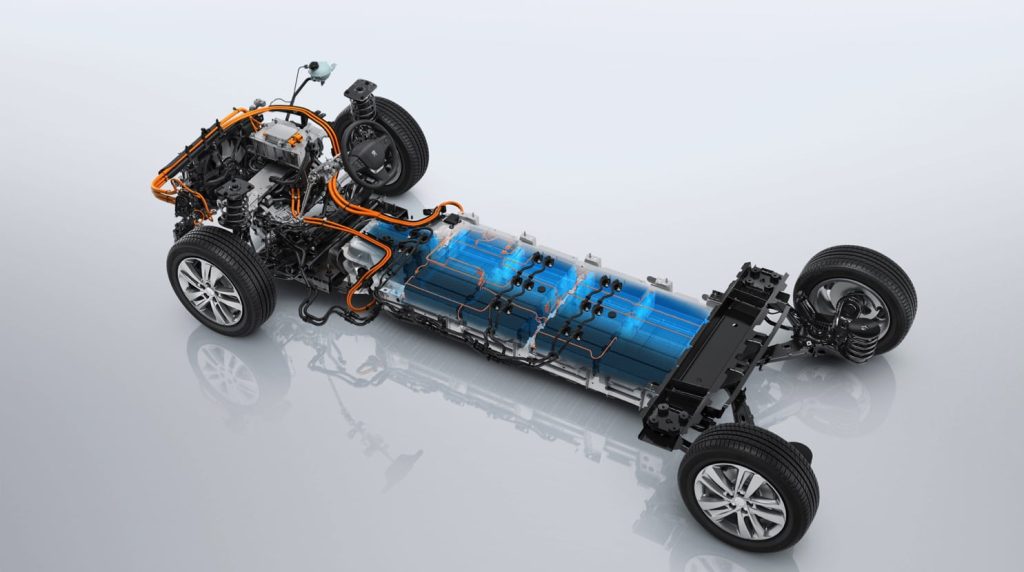

Power Electronics and Inverter: Electric cars feature power electronics and inverters that play a crucial role in managing the flow of electricity between the battery and the electric motor. The inverter converts the direct current (DC) stored in the battery into alternating current (AC) used by the electric motor.
Electric Vehicle Control Unit (VCU): The Electric Vehicle Control Unit acts as the brain of the electric car, coordinating the various components to optimize performance, efficiency, and safety. From managing battery temperature to controlling the power output, the VCU ensures a seamless and reliable driving experience.

The Driving Experience: Beyond the mechanics, the driving experience of an all-electric car is a revelation. Instant torque delivery provides swift acceleration, and the absence of engine noise creates a serene environment for passengers. With fewer moving parts, electric cars often require less maintenance, contributing to their appeal.
Conclusion: All-electric cars represent the vanguard of a cleaner, more sustainable future in transportation. As technology advances and infrastructure continues to grow, the electric revolution is set to transform not just the way we drive but also our impact on the environment. The synergy of electric motors, advanced batteries, and smart control systems is propelling us towards a future where the roads are not just navigated but navigated sustainably.
temp mail
This resource is fabulous. The wonderful data exhibits the essayist’s earnestness. I’m stunned and expect more such astonishing presents.
estepan
Thank you so much for your lovely comment.
Domenico Medhurst
Your blog is a treasure trove of valuable insights and thought-provoking commentary. Your dedication to your craft is evident in every word you write. Keep up the fantastic work!
Melisa Huel
Your writing is like a breath of fresh air in the often stale world of online content. Your unique perspective and engaging style set you apart from the crowd. Thank you for sharing your talents with us.
Queen Kiehn
Thank you I have just been searching for information approximately this topic for a while and yours is the best I have found out so far However what in regards to the bottom line Are you certain concerning the supply
Valeria Valenzuela
Excellent tips — I implemented a few and saw immediate improvement.
Paisley Franklin
Nice balance of theory and practical advice. Well done!
Roberto Mcgee
I never thought about it this way before. Your post gave me a fresh perspective.
Kamari Decker
Strong points and clear examples. Please write more on this topic.
Reader_2023
Definitely one of the best explanations out there.
Alec Mayo
Informative and well-referenced. Do you have a resource list?
Sylvia Todd
Great perspective — I hadn’t considered that angle before.
Londyn Larsen
Thanks for breaking this down into simple steps — very useful.
Fiona Conway
Great mix of research and practical application. Very helpful.
Morgan Galvan
This was a delightful and educational read — thanks for sharing!
Blaine Ingram
Insightful post — I’d be interested in a follow-up on advanced topics.
ropa segunda mano
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
Lillianna Mccarty
Excellent roundup of resources — saved me hours of searching.
segunda mano
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
alquiler pisos
I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I assumed this publish used to be great
Julia Ali
This topic is so relevant right now. Thanks for the timely post.
rize en iyi restoran
Kuru fasulye hem taze hem de sıcak geldi, servis hızlıydı. Gerçekten ev yapımı hissi veren bir lezzet. Rize’de böyle bir kaliteyi bulmak zor.
Luna Mccullough
Your tone is friendly and informative — made for an enjoyable read.
Cloe Ward
This article is well-researched and clearly written. Appreciate the effort!
Junius Gaylord
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
Valeria Valenzuela
Nice balance of theory and practical advice. Well done!
Aliyah Madden
This really cleared up confusion I had. Much appreciated!
Augustus Potter
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Malaki Kerr
Thanks for the helpful checklist — it made planning simpler.
Abby Conner
Appreciate the time you put into this — it’s packed with value.
Amiya Lynch
Thank you for such a thorough and thoughtful article.
Brogan Ortega
I appreciate the honesty in your assessment — refreshing to see.
Jaxson Bates
Informative and well-referenced. Do you have a resource list?
Kaley Mejia
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Cali Pierce
Fantastic post — I shared it with my team and they found it useful.
Skyler Hinton
This topic is so relevant right now. Thanks for the timely post.
Heidy Mercer
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Cara Livingston
Fantastic post — I shared it with my team and they found it useful.
Seth Sanders
Very actionable advice. I can start applying this right away.
Jamarcus Eaton
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Jazmyn Solis
Well-researched and balanced. Appreciate the effort behind this.
Israel Gomez
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
Ricky Sanford
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Harold Hardin
This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.